Is Light Necessary for Seed Germination?
Fundamentally, it is common knowledge that light is necessary for seed germination. Also, if you’ve tried germinating seeds indoors, you’d have observed the need for grow lights since sunlight is not available.
However, it is interesting to note that some plants do not require light for their seed-germination process.
For plants to thrive, they need three basic requirements, soil, water, and light. These elements are needed in the right amount to sponsor photosynthesis for sprouting seeds; light is sometimes not required for this process. The reason is, that some plants do better in darkness than with sunlight.
This article will answer all your questions regarding the necessity of light for seed germination and much more; read till the end.
- Part 1: What Is Seed Germination?
- Part 2: Seed Germination Stages
- Part 3: What Do Seeds Need to Germinate Successfully?
- Part 4: Is Light Even Necessary?
- Part 5: Seeds That Need Light to Germinate
What Is Seed Germination?
By basic definition, seed germination is the process in which seeds grow into fully mature plants. What happens during this process ends up influencing both the seed quality and that of the plant.
Remember that for this to happen, some environmental factors have to trigger the event.
So, how the seed grows is affected by how you plant it, the temperature around it, humidity, and much more.
Generally, plants can be classified based on the type of germination they undergo. The classification, in this case, is based on how the cotyledons are present (the first leaf the sprouted seeds get to produce). These two types include:
- Epigeal germination
- Hypogeal germination
In epigeal germination, the cotyledon breaks out through the soil as a result of the elongation and rapid growth of the early part of the stem (hypocotyl). This type of germination is very common in plants like beans and castor.
While in hypogeal germination, the cotyledons remain buried within the soil as a result of the quick sprouting of the epicotyl (the part of the stem of the sprouting plant just above the cotyledon).

Image Source: plantscience4u.com
A seed germination diagram will best explain the already highlighted types of seed germination.
Let’s take a look at the seed germination stages now.
Seed Germination Stages
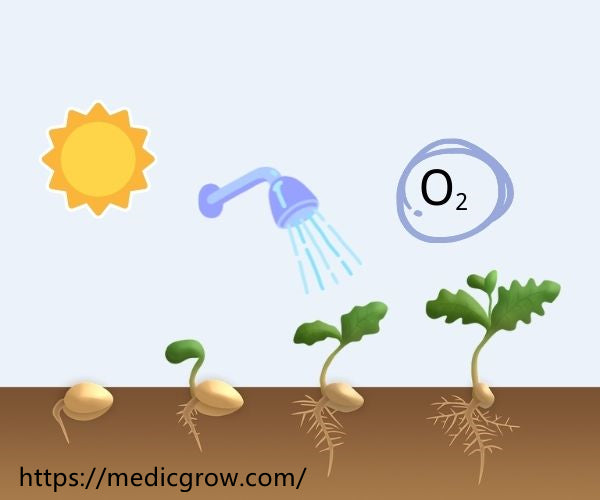
For a seed to properly germinate, it needs to go through this entire process:

Image Source: sciencefacts.net
1. The absorption stage:
This stage is also called the imbibition stage; it is where the dry seeds get to absorb water and swell. The result of this swelling causes the seed coat to break or rupture.
2. Oxygen Intake, Respiration, & Metabolic Phase:
As a result of the imbibition of water in the first stage, metabolic activity is triggered within the seed. Then, the process of aerobic respiration sets in because the seed initially does not have oxygen.
Also, at this stage of seed germination, the seed requires some level of energy to continue with the growth process. This energy comes from glycolysis.
Glycolysis is the breakdown of glucose within the plant so that there can be a release of energy for vital functions.

Image Source: thoughtco.com
So, oxygen then begins to find its way into the seed, and respiration becomes aerobic. For most plants that thrive on land, the source of their oxygen is usually the air from the soil on which they are planted. The knowledge of this is what informs plowing and loosening of the soil before sowing.
For seeds that grow in water, they derive their oxygen from the dissolved oxygen in the water.
3. The Light Absorption Phase:This stage is a distinguishing phase for most plants as they have different responses to light for their germination. Some plants are photoblastic (they grow in the light), while others are non-photoblastic (they don’t need light to grow).
When seeds have absorbed water and oxygen, they tend to respond better to light, and if they are positively photoblastic, then just the right amount of light will provoke their growth. The reason for this is that these light-dependent plants contain a pigment known as phytochrome which helps with the absorption.
4. Utilization of the reserved nutrient during seed germination:
At the early stage of development, the cotyledons are responsible for storing food. When the process of germination proceeds, the stored proteins, fats, and carbohydrates are then digested to release energy for metabolism.
This energy is also required for cell divisions within the sprouting seeds via aerobic respiration.
The seedling/embryo can only absorb or digest food compounds in bits and so, enzymes help to break these nutrients down. These enzymes include proteases, amylases, etc. They make food usable and absorbable by the plants.
Other growing parts of the growing seedling get their share of the nutrients by the translocation of the soluble food materials by water. Examples of such parts are the plumule and the radicle.
5. Growth from embryo to seedling:
When food is evenly distributed throughout the plant, growth continues unhindered. Nutrients getting to the radicle make for its rapid development into the root. It grows downwards, deep into the soil, and then starts to absorb minerals and water from it.
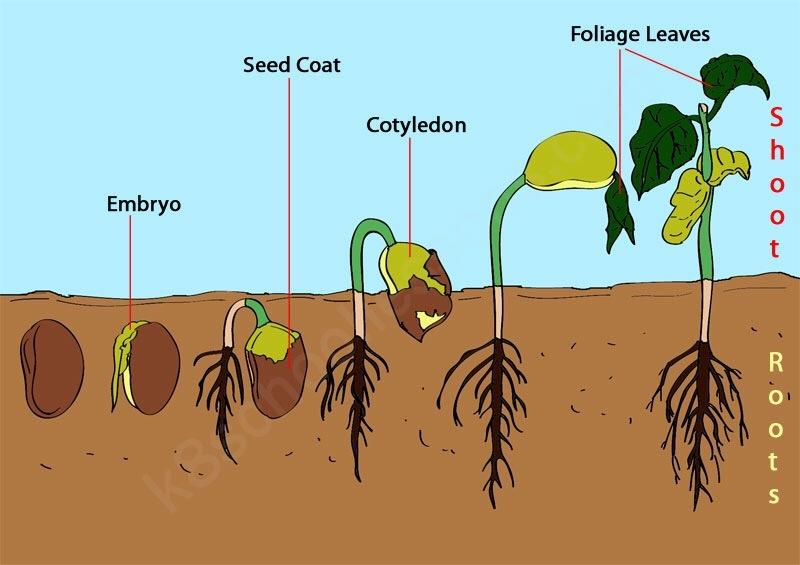
The next thing is the growth of the plumule. The plumule grows upwards after receiving nutrients and becomes the shoot. When it gets above the soil, it develops green leaves that eventually produce its food through photosynthesis.
What Do Seeds Need to Germinate Successfully?
For a seed to become a seedling and then a mature plant, here are the requirements needed:
1. Moisture:
You can't talk about seed germination without talking about water. Remember that the first stage of development for any seed is the absorption of water.
Some seeds are relatively dry, and for them to begin germinating, they need to absorb much water. Water helps with the following during seed germination:
- It helps to transport nutrient
- It provides dissolved oxygen for the embryo
- It makes it easy for the cotyledons to break out from the seed coat
- It helps to sponsor metabolic activities within the seedling
2. Light:
Honestly, light is much a vital requirement for some plants as darkness is to others; it all depends on the nature of the plant in question.
Light serves as an external trigger for the seed germination process, and some plants would not sprout till light shines on them.

3. Temperature:
The temperature required for a seed to germinate fluctuates between 25-30°C. Not all seeds will require this temperature to grow, while others will require much more. However, the range of temperature considered to be optimal is between 5 to 40°C.
Temperature also determines the seed germination time for some plants since some seeds are planted outdoors and are left to thrive on their own.
4. Air/ Oxygen:
Oxygen is needed for energy and metabolism; it is essential for seed germination. Aerobic respiration is the primary and initial respiration mode undertaken by plants before they can eventually produce their nutrients.
The role of oxygen also determines how certain seeds are planted; when some seeds are buried too deep within the soil, they don’t thrive.
Is Light Even Necessary?
Most plants are phototropic, which means that they move in the direction of light. All plants require light to grow their root, and if they're deprived of this, their roots become leggy due to their strain on sunlight.
There is, however, a variation in the amount of light required for each plant.
For plants that require less UV light for plants during their adult life, they won’t require as much light as compared to others. When seedlings are overly exposed to heat and sunlight, they dry up or die.
When it comes to seed germination, some seeds need light, while others don’t. This knowledge helps us decide when to begin growing seeds indoors or even outdoors.
If you've thought of growing your plants indoors, then you need to be aware that plants that require light to sprout may greatly benefit from LED grow lights.
Importance of Led Grow Lights for Indoor Plants
Among indoor plant growers, full-spectrum LED grow lights have become popular for many reasons. One of which is the numerous benefits it confers. Here are some of the benefits.

Longer Lifespan:
LED grow lights can help simulate or recreate the same atmosphere that sunlight provides for seed germination. Most LED grow lights have a longer lifespan and last long, and you can rest assured that your plants are getting quality light exposure.
Cooler Temperature:
Unlike HID bulbs, LED grow lights emit less heat and have less potential to damage your plant with extreme temperature/light.
Efficiency:
Indoor plant growers admit that LED grow lights are more efficient in their contribution to the growth process of indoor plants.
Seeds That Need Light to Germinate
We’ve gone to two, talking about how important light is in the growth of plants. Now, let’s look at a list of plants that require light for their development, shall we?
- Impatiens
- Columbine
- Balloon flower
- Coleus
- Lettuce
- Lobelia
- Petunias
- Gaillardia
- Browallia
- Nicotiana
- Snapdragons
- Savory
- Osteospermum, etc.
Conclusion
Seed germination is a fun process for the gardener, and having the right knowledge makes things easy. For seeds to thrive, they require optimum levels of light, temperature, moisture, etc., at the most fundamental level.
Not all seeds require light to grow, while others that do should be given the right amount of light, especially seedlings.
It is possible to cultivate your plants indoors; 800W LED grow lights would be of great benefit here. However, never forget that excess exposure to light and heat can dry up the plant and lead to death.
Ready to begin your seed germination process? The best time to kick off is now.
Related Posts:
What is Light Burn: How to Fix it?
How Much Light Do Indoor Plants Need?
Featured Products
Blog Posts
Contact Us with Any Idea!
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
!